Similar to the delayed neutron measurements, delayed gamma
techniques utilize measurements of beta-delayed isotopes that are
produced in fission events. Delayed gamma rays are emitted from
particular fission products following beta-decays, and therefore
have distinguishing time scales associated with emission. The
differences in the distribution of fission product yields can be
used to quantify and distinguish each fissile element. The DG
system works by interrogating a spent fuel assembly with a neutron
source, commonly a Deuterium-Tritium source compatible with most
active interrogation techniques, and using a high-purity germanium
(HPGe) detector to measure the delayed gamma peaks. An
example of a DG spectra is shown in Figure 28 for a depleted
uranium sample (i.e. almost entirely 238U).
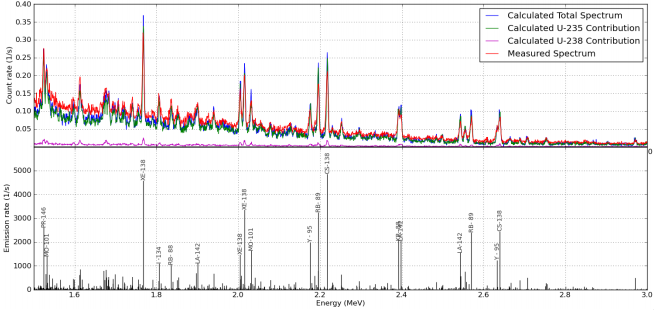
Figure
28. Calculated (bottom) and measured (top) spectra of delayed-gamma
from depleted uranium (
In order to isolate the relevant gamma peaks from the spectra,
previous knowledge is needed of the energy of the delayed gammas
specific to the material being investigated. The isolation of
the DG peaks can be a challenge due to interferences with passive
gamma radiation from the spent fuel. Current work is
concentration on minimizing interferences, such as by better
optimizing the detector setup. Other efforts are focused on
better characterizing the differences in the DG spectra for unique
spent fuel compositions.
Source:
- V. Mozin, L. Campbell, A. Hunt, B. Ludewigt, "Delayed Gamma-Ray
Spectroscopy for Spent Nuclear Fuel Assay," Journal of
Nuclear Materials Management 40:3 (2012).
- V. Mozin, S. Tobin, L. Cambell, J. Cheatham, C. Freeman, C.
Gesh, A. Hunt, B. Ludewigt, E. Reedy, H. Selpel, L. Smith, J.
Sterbentz, J. Vujic, J. White, P. Blanc, S. Croft, J. Conlin, L.
Evans, M. Fensin, J. Hu, T. Lee, A. LaFleur, H. Menlove, M. Schear,
M. Swinhoe, W. Koehler, J. Richard, N. Sandoval, and S. Thompson,
"Determining Plutonium Mass in Spent Fuel with Non-destructive
Assay Techniques - NGSI Research Overview and Update on NDA
Techniques, Part II," IAEA Safeguards Symposium, IAEA-CN-184/137,
2010. See document.