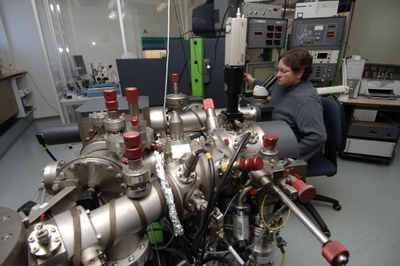
Expert performing isotopic measurements on uranium particles with Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometer (SIMS) at the Seibersdorf Analytical Laboratory in Austria.
(Source:
Dean Calma/IAEA)
A technique for measuring the isotopic composition of nuclear
material in micrometer size environmental particles by mounting
them on a conducting substrate and bombarding them in vacuum with
energetic ions. This results in the ejection of secondary ions
which are analyzed by a mass spectrometer to measure the isotopic
composition of uranium and plutonium in the particle.